Describe Two Important Functions of the Large Intestine
The large intestine goes into a more deeper form of digestion and removes water and other moisture from the waste. In the small intestine partially digested food which has been reduced to a slurry called chyme is mixed with intestinal juices.

Large Intestine Ppt Video Online Download
The organ takes approximately 16 hours to complete the digestion of food.
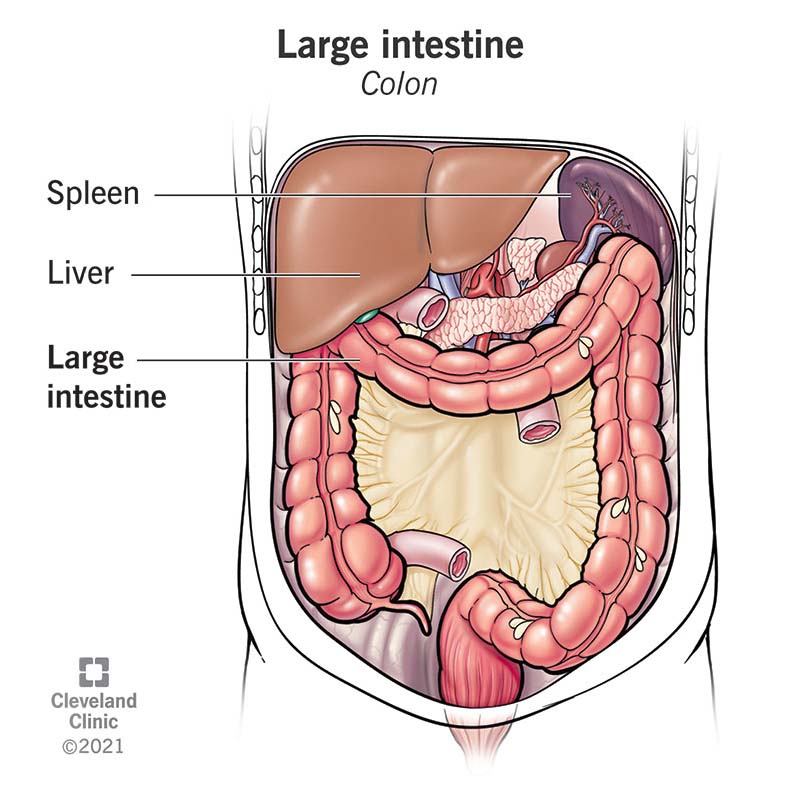
. The ileum receives the food from the jejunum and empties into the large intestine. What are the 4 major functions of the large intestine. Haustral churning peristalsis and mass peristalsis drive contents of colon into rectum.
Absorption of some water ions and vitamins. Absorption of water so as to convert the liquefied indigestible matter into faecal matter. A slurry of digested food known as chyme enters the large intestine from the small intestine via the ileocecal sphincter.
This organ is the last part of the digestive system and stretches from the ileocecal valve to the anus. The function of the large intestine The large intestine stores the wastes the food remains then ejects them outside the body through the anus. By the time indigestible materials have reached the colon most nutrients and up to 90 of the water has been absorbed by the small intestine.
Chyme passes through the cecum where it is mixed with. Haustral and antiperistaltic contractions help it absorb water and electrolytes. The large intestine is the terminal part of the alimentary canal.
- Store and transport undigested material. The small intestine absorbs water and nutrients and it prepares the food for the next step in digestion the large intestine. Describe 2 important functions of the small intestine.
It has 4 regions. Reabsorbing water and maintaining the bodys balance of fluids. Provide a detailed description of the path of chyme and later feces from the duodenum to the anus identifying the different portions of the small and large intestines.
Many people think of the large intestine as simply a storage organ a conduit for carrying indigestible nutrients from the small intestine to the anus to be discharged yet this organ has many very important functions in the gastrointestinal GI tract including. Water nutrients and salts from food to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. The large intestine consists of the cecum and colon.
Reabsorb water and compact feces. Large Intestine Large Intestine Digestion is the process of break down of complex food materials into simpler substances which can be absorbed by blood and transported throughout the body. The organ is also an essential part of the immune system.
What are two major functions of the large intestine. Caecum colon rectum and anal canal. Absorbing water and electrolytes producing and absorbing vitamins and forming and propelling feces toward the rectum for elimination.
The large intestine prepare. The body has two types of intestines. The large intestine is where faeces form from food residues water and bodily by-products.
It continues the process of absorption via the intestinal wall villi absorbing any products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. Provide a detailed description of the path of chyme and later feces from the duodenum to the anus identifying the different portions of the small and large intestines. The primary function of the small intestine is to continue the process of digestion that began in the mouth and the stomach.
The organs that make up the digestive tract include. The large intestine is the final section of the gastrointestinal tract that performs the vital task of absorbing the water and the vitamins and it converts the digested food into feces. Motility digestion absorption and secretion are the four vital functions of the digestive system.
Based on your knowledge of its location in the abdomen in which of. The small intestine is connected to the stomach and handles the middle part of the digestion process. In the large intestine poor motility can lead to ____ and excess motility can lead to ____.
Bacteria in large intestine convert proteins to amino acids break down amino acids and produce some B vitamins and. Diverticulitis most often affects the sigmoid colon. The large intestine comprises the caecum colon rectum anal canal and anus.
Richard ClarkEGetty Images The main function of the large intestine is to absorb water and remove solid waste from the body. - Absorb water and electrolytes. Diverticulitis most often affects the sigmoid colon.
Mass movements push faeces towards the anus and create an urge to defecate. Absorb vitamins by bacteria. The function of the large intestine or large bowel is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and then to pass the useless waste material from the body.
Functions of Large Intestine. The large intestine also called the colon is part of. The digestive system breaks down the foods we eat into energy our bodies can use.
The large intestine performs the vital functions of converting food into feces absorbing essential vitamins produced by gut bacteria and reclaiming water from feces. The digestion process releases energy which is utilized. Describe 2 important functions of the small intestineDescribe 2 important functions of the large intestine.
Functions of the large intestine. The complex symbiotic relationships between bacteria in the large intestine produce vitamins the body needs. - Eliminate undigested material.
- Absorb short chain fatty acids. The length of large intestine is about 15 m. The primary function of this organ is to finish absorption of nutrients and water synthesize certain vitamins as well as to form store and eliminate feces from the body.
Main functions of the large intestine. Toxic metals and other toxins are secreted into the faecal matter in the region of large intestine. The large intestines function is much more complex than forming stool.
The large intestine has 3 primary functions. Store fecal material prior to defacation divisions of large intestine.

Question Video Describing The Function Of The Large Intestine Nagwa
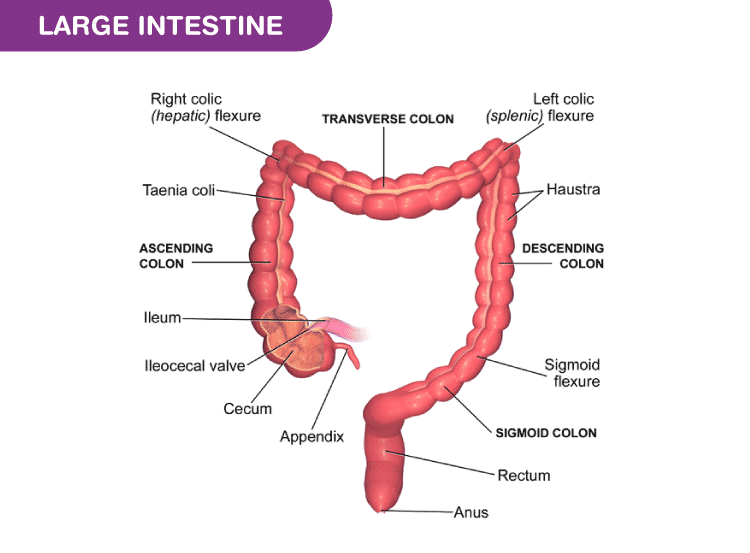
Large Intestine Structure And Functions

Large Intestine Definition Location Anatomy Length Function Facts Britannica
No comments for "Describe Two Important Functions of the Large Intestine"
Post a Comment